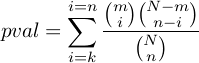
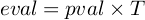
E-value represents the Expected number of false positive in multiple testing.
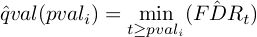
where t is the threshold for P-values below which the TF is called significant.
According to Storey et al. : a q-value threshold can be phrased in paractical terms as the proportion of the significant features (here TF) that trun out to be false leads.
- Rank ascending the P-values of the tests;
- Compute for each P-value the corresponding FDR control:
- find the largest rank i for which the P-value <= FDR Control
- all the tests with ranked P-values from 1 to i are considered as significant under this FDRt
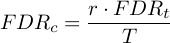
where r is the rank of the P-value
and FDRt is the specified FDR Threshold.
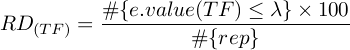
where λ represents the e-value threshold, and rep stands for repetitions.
RC represents a non parametric control of false positives.